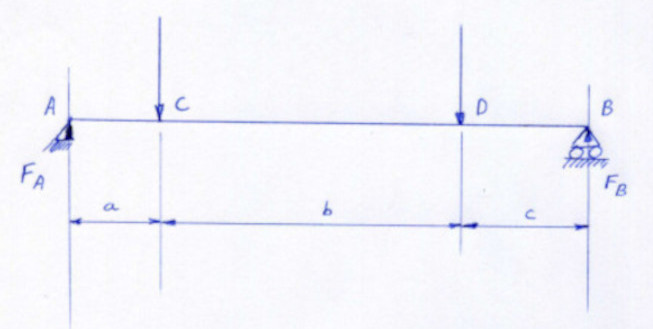
| Line load due to the own weight of the shaft |
? |
N/mm |
| Total length of the shaft |
? |
mm |
| |
| T_A (transverse force in A) |
? |
N |
| T_C21 (transverse force 1 in C) |
? |
N |
| T_C22 (transverse force 2 in C) |
? |
N |
| T_D21 (transverse force 1 in D) |
? |
N |
| T_D22 (transverse force 2 in D) |
? |
N |
| T_B (transverse force in B) |
? |
N |
| Lowest value of T_A,T_C21,T_C22,T_D21, T_D22, T_B |
? |
N |
| Highest value of T_A,T_C21,T_C22,T_D21, T_D22, T_B |
? |
N |
| |
| Reaction force FA |
? |
N |
| Reaction force FB |
? |
N |
| |
| Location of the maximum bending moment |
? |
|
| Location of zero on the transverse force line |
? |
mm |
| Maximum bending moment |
? |
Nmm |
| |
| Deflection in the middle of the shaft |
? |
mm |
| Maximum deflection in the entire shaft (40 evaluation points) |
? |
mm |
| Maximum deflection in the entire shaft at distance |
? |
mm |
| Deflection limit based on total length/300 |
? |
mm |
| |
| Required moment of resistance W |
? |
mm3 |
| Required diameter d |
? |
mm |