| d predetermined |
? |
mm |
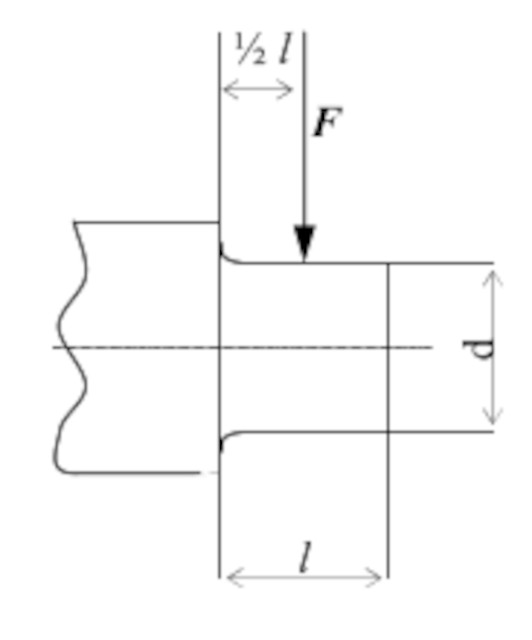
| According length l of the stub = dpredetermined.sqrt((π.σb)/(16.σ0)) |
? |
mm |
| |
|
|
| Diameter dsurface pressure = 4.F/(π.σ0.lpredetermined) |
? |
mm |
| According length l of the stub = dsurface pressure.sqrt((π.σb)/(16.σ0)) |
? |
mm |
| |
|
|
| Diameter d for bending = (16.F.lpredetermined/(π.σb))^(1/3) |
? |
mm |
| According length l of the stub = dbending.sqrt((π.σb)/(16.σ0)) |
? |
mm |
| |
|
|
| Required length l of the stub l for heat dissipation : F.n/w |
? |
mm |
| Is cooling oil required? |
? |
|
| Circumferential speed of the stub = π.dpredetermined.n/60000 |
? |
m/s |
| Friction labour = 0,05.F.v.3,6 |
? |
kJ/h |
| Required cooling oil = friction labour/(specific heat cooling oil.ΔT) |
? |
kg/h |